2023-05-15:对于某些非负整数 k ,如果交换 s1 中两个字母的位置恰好 k 次, 能够使结果字符串等于 s2 ,则认为字符串 s1 和 s2 的 相似度为 k。 给你两个字母异位词 s1
2023-05-15:对于某些非负整数 k ,如果交换 s1 中两个字母的位置恰好 k 次,
能够使结果字符串等于 s2 ,则认为字符串 s1 和 s2 的 相似度为 k。
给你两个字母异位词 s1 和 s2 ,返回 s1 和 s2 的相似度 k 的最小值。
输入:s1 = "abc", s2 = "bca"。
输出:2。
答案2023-05-15:
解题思路:
-
定义一个小根堆,按照节点的估值函数进行排序。
-
初始化节点为 s1,将其加入小根堆。同时记录访问过的节点,以避免重复搜索。
-
从小根堆中弹出代价最小的节点 cur。
-
如果 cur 与 s2 相等,则返回当前代价 cost。
-
否则,找到 cur 与 s2 第一个不同的位置 firstDiff,再枚举 firstDiff 之后的位置 i。
-
如果 cur[i] 与 s2[firstDiff] 相等但不在第 i 个位置,则构造一个新的字符串 newStr,交换 newStr[firstDiff] 和 newStr[i] 的位置。
-
将 newStr 加入小根堆,代价是 cost+1,where 是 firstDiff+1。
-
在加入前判断是否已经访问过,如果访问过就跳过该节点。
-
将 newStr 和 cur 恢复为原始状态(恢复数组)。
-
重复上述步骤,直到小根堆为空或者找到相同的字符串。
需要注意的点:
-
估值函数的实现是可以调整的,可以根据实际情况来实现更加合适的估值函数。
-
在 Go 中没有提供 C 语言中的 strdup 函数。可以使用 string 转换为字节数组 []byte,然后再转换为字符串。
-
在 Go 中 map 是无序的,如果想要按照访问顺序遍历可以在 Node 中增加一个 visited 字段,每次入队时设置 visited = true,在出队时判断 visited 是否为 true,如果为 true 则跳过。
时间复杂度为O(n^2),其中n是字符串的长度。
空间复杂度为O(n^2),存储小根堆和visited哈希表所需的空间。
go完整代码如下:
package main
import "fmt"
type Node struct {
cost int
guess int
where_ int
str_ string
}
func kSimilarity(s1 string, s2 string) int {
len := len(s1)
heap := &NodeHeap{}
visited := make(map[string]struct{})
heap.Push(&Node{0, 0, 0, s1})
for heap.Len() > 0 {
cur := heap.Pop().(*Node)
if _, ok := visited[cur.str_]; ok {
continue
}
if cur.str_ == s2 {
return cur.cost
}
visited[cur.str_] = struct{}{}
firstDiff := cur.where_
for firstDiff < len && cur.str_[firstDiff] == s2[firstDiff] {
firstDiff++
}
curStr := []byte(cur.str_)
for i := firstDiff + 1; i < len; i++ {
if curStr[i] == s2[firstDiff] && curStr[i] != s2[i] {
swap(curStr, firstDiff, i)
add(string(curStr), s2, cur.cost+1, firstDiff+1, heap, visited)
swap(curStr, firstDiff, i)
}
}
}
return -1
}
type NodeHeap []*Node
func (h NodeHeap) Len() int { return len(h) }
func (h NodeHeap) Less(i, j int) bool {
return h[i].cost+h[i].guess < h[j].cost+h[j].guess
}
func (h NodeHeap) Swap(i, j int) { h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i] }
func (h *NodeHeap) Push(x interface{}) {
*h = append(*h, x.(*Node))
}
func (h *NodeHeap) Pop() interface{} {
old := *h
n := len(old)
x := old[n-1]
*h = old[0 : n-1]
return x
}
func add(add string, s2 string, cost int, index int, heap *NodeHeap, visited map[string]struct{}) {
if _, ok := visited[add]; !ok {
heap.Push(&Node{cost, evaluate(add, s2, index), index, add})
}
}
func swap(s []byte, i int, j int) {
tmp := s[i]
s[i] = s[j]
s[j] = tmp
}
func evaluate(s1 string, s2 string, index int) int {
diff := 0
for i := index; i < len(s1); i++ {
if s1[i] != s2[i] {
diff++
}
}
return (diff + 1) / 2
}
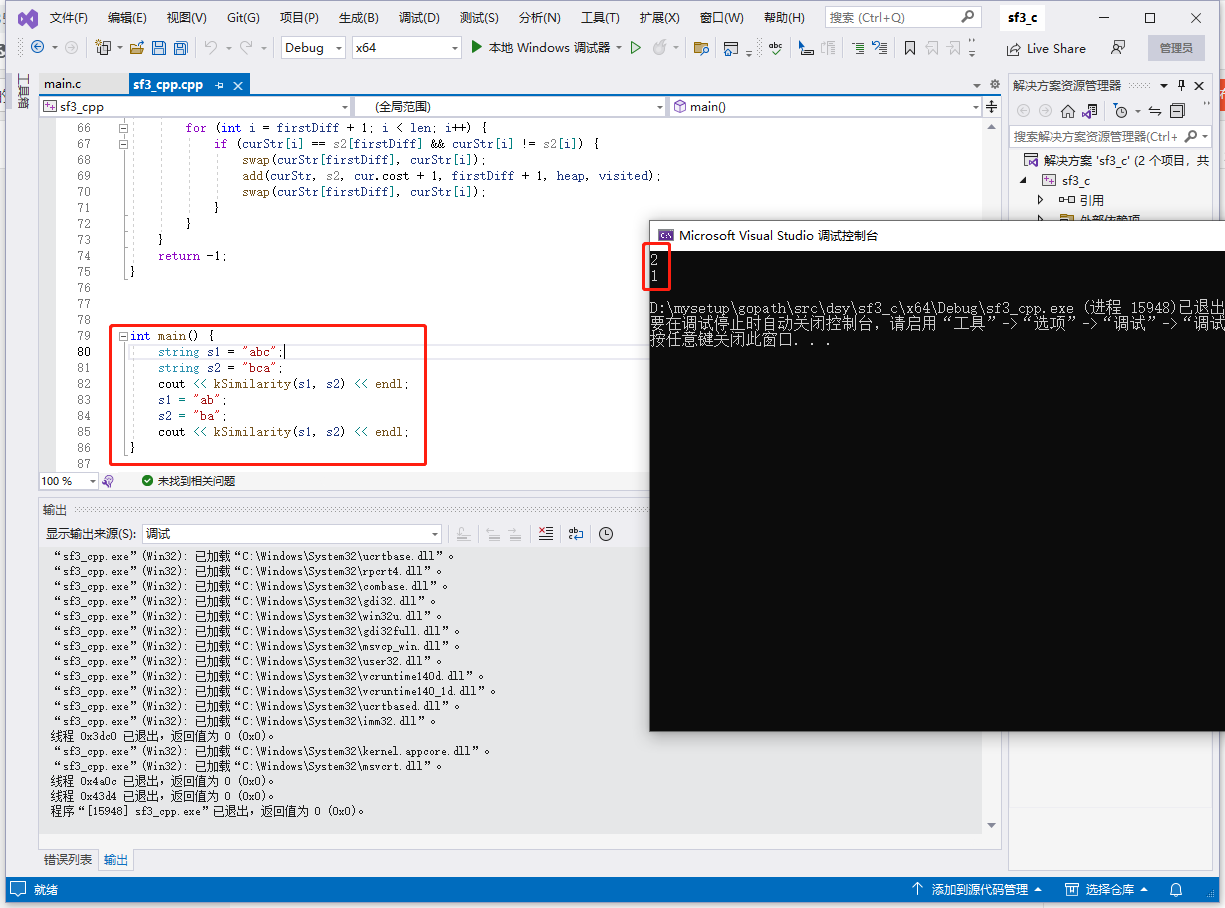
func main() {
s1 := "abc"
s2 := "bca"
fmt.Println(kSimilarity(s1, s2))
s1 = "ab"
s2 = "ba"
fmt.Println(kSimilarity(s1, s2))
}
rust完整代码如下:
#[derive(Eq, PartialEq)]
struct Node {
cost: i32,
guess: i32,
where_: usize,
str_: String,
}
impl Ord for Node {
fn cmp(&self, other: &Self) -> std::cmp::Ordering {
(self.cost + self.guess).cmp(&(other.cost + other.guess))
}
}
impl PartialOrd for Node {
fn partial_cmp(&self, other: &Self) -> Option<std::cmp::Ordering> {
Some(self.cmp(other))
}
}
fn k_similarity(s1: String, s2: String) -> i32 {
let len = s1.len();
let mut heap = std::collections::BinaryHeap::new();
let mut visited = std::collections::HashSet::<String>::new();
heap.push(Node {
cost: 0,
guess: 0,
where_: 0,
str_: s1,
});
while let Some(cur) = heap.pop() {
if visited.contains(&cur.str_) {
continue;
}
if cur.str_ == s2 {
return cur.cost;
}
visited.insert(cur.str_.clone());
let mut first_diff = cur.where_;
while cur.str_.chars().nth(first_diff).unwrap() == s2.chars().nth(first_diff).unwrap() {
first_diff += 1;
}
let cur_str = cur.str_.as_bytes();
for i in first_diff + 1..len {
if cur_str.get(i).unwrap() == &s2.as_bytes()[first_diff]
&& cur_str.get(i).unwrap() != &s2.as_bytes()[i]
{
let mut new_str = String::from_utf8_lossy(cur_str).to_string();
swap(&mut new_str, first_diff, i);
add(
new_str,
s2.clone(),
cur.cost + 1,
first_diff + 1,
&mut heap,
&visited,
);
}
}
}
-1
}
fn swap(s: &mut String, i: usize, j: usize) {
unsafe {
let s_mut = s.as_mut_vec();
let tmp = std::ptr::read(s_mut.get_unchecked(i));
std::ptr::copy_nonoverlapping(s_mut.get_unchecked(j), s_mut.get_unchecked_mut(i), 1);
std::ptr::write(s_mut.get_unchecked_mut(j), tmp);
}
}
fn add(
add: String,
s2: String,
cost: i32,
index: usize,
heap: &mut std::collections::BinaryHeap<Node>,
visited: &std::collections::HashSet<String>,
) {
if !visited.contains(&add) {
heap.push(Node {
cost,
guess: evaluate(&add, &s2, index),
where_: index,
str_: add,
});
}
}
// 估值函数
// 看每周有营养的大厂算法面试题,2022年1月第3周
// 估值函数的估计值要绝对 <= 真实距离
// 但又要确保估计值足够大足够接近真实距离,这样效果最好
fn evaluate(s1: &str, s2: &str, index: usize) -> i32 {
let mut diff = 0;
for i in index..s1.len() {
if s1.chars().nth(i).unwrap() != s2.chars().nth(i).unwrap() {
diff += 1;
}
}
(diff + 1) as i32 / 2
}
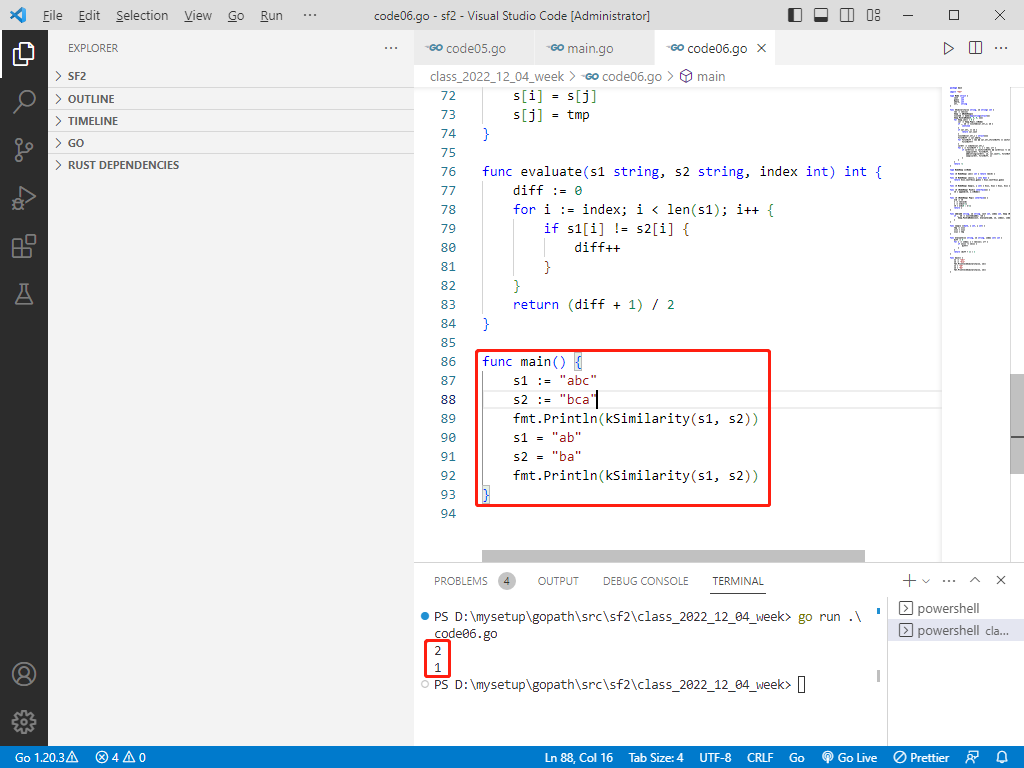
fn main() {
let s1 = String::from("abc");
let s2 = String::from("bca");
println!("{}", k_similarity(s1, s2));
let s1 = String::from("ab");
let s2 = String::from("ba");
println!("{}", k_similarity(s1, s2));
}
c完整代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef struct Node {
int cost; // 代价,已经换了几回了!
int guess;// 猜测还要换几回,能变对!
int where;// 有必须去比对的下标,左边不再换了!
char* str; // 当前的字符
} Node;
int CompareNode(const void* a, const void* b) {
Node* pa = (Node*)a;
Node* pb = (Node*)b;
return (pa->cost + pa->guess) - (pb->cost + pb->guess);
}
void swap(char* a, char* b) {
char tmp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = tmp;
}
int evaluate(char* s1, char* s2, int index, int len) {
int diff = 0;
for (int i = index; i < len; i++) {
if (s1[i] != s2[i]) {
diff++;
}
}
return (diff + 1) / 2;
}
void add(char* add, char* s2, int cost, int index, Node* heap, int heapSize,
char** visited, int* visitedSize) {
for (int i = 0; i < *visitedSize; i++) { // 判断是否已经访问过
if (strcmp(add, visited[i]) == 0) {
return;
}
}
Node next;
next.cost = cost;
next.guess = evaluate(add, s2, index, strlen(add));
next.where = index;
next.str = _strdup(add);
heap[heapSize] = next;
qsort(heap, heapSize + 1, sizeof(Node), CompareNode); // 排序小根堆
visited[*visitedSize] = _strdup(add);
(*visitedSize)++;
}
int kSimilarity(char* s1, char* s2) {
int len = strlen(s1);
Node* heap = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node) * len * len); // 分配空间
int heapSize = 0;
char** visited = (char**)malloc(sizeof(char*) * len * len); // 分配空间
int visitedSize = 0;
add(s1, s2, 0, 0, heap, heapSize++, visited, &visitedSize);
while (heapSize > 0) {
Node cur = heap[0];
Node tmp = heap[--heapSize]; // 最后一个节点移到根节点,并下移
heap[0] = tmp;
int index = 0;
while (index * 2 + 1 < heapSize) {
int left = index * 2 + 1;
int right = index * 2 + 2;
int min = left;
if (right < heapSize && (heap[right].cost + heap[right].guess) < (heap[left].cost + heap[left].guess)) {
min = right;
}
if ((heap[index].cost + heap[index].guess) > (heap[min].cost + heap[min].guess)) {
tmp = heap[index];
heap[index] = heap[min];
heap[min] = tmp;
index = min;
}
else {
break;
}
}
if (strcmp(cur.str, s2) == 0) {
int cost = cur.cost;
free(cur.str);
for (int i = 0; i < heapSize; i++) {
free(heap[i].str);
}
free(heap); // 释放内存
for (int i = 0; i < visitedSize; i++) {
free(visited[i]);
}
free(visited);
return cost;
}
int firstDiff = cur.where;
while (cur.str[firstDiff] == s2[firstDiff]) {
firstDiff++;
}
for (int i = firstDiff + 1; i < len; i++) {
if (cur.str[i] == s2[firstDiff] && cur.str[i] != s2[i]) {
char* newStr = _strdup(cur.str); // 复制字符串
swap(&newStr[firstDiff], &newStr[i]); // 交换字符
add(newStr, s2, cur.cost + 1, firstDiff + 1, heap, heapSize++, visited, &visitedSize); // 加入新节点
swap(&newStr[firstDiff], &newStr[i]); // 恢复字符串
}
}
free(cur.str);
}
for (int i = 0; i < heapSize; i++) {
free(heap[i].str);
}
free(heap); // 释放内存
for (int i = 0; i < visitedSize; i++) {
free(visited[i]);
}
free(visited);
return -1;
}
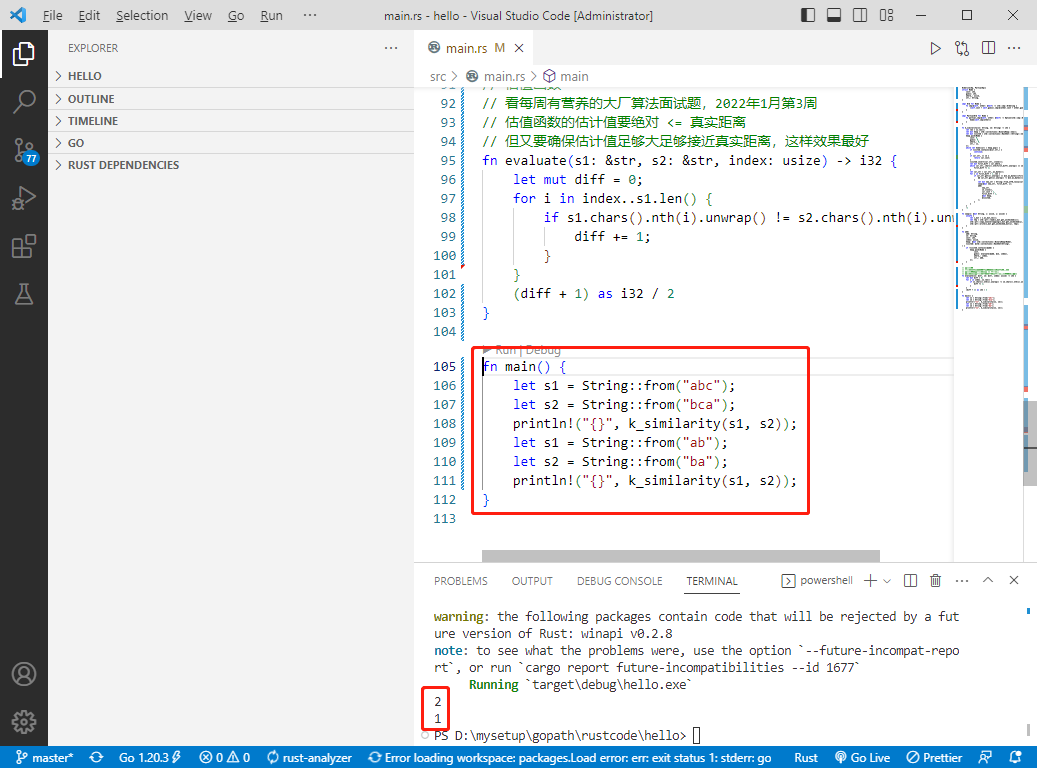
int main() {
char s1[] = "abc";
char s2[] = "bca";
printf("%d\n", kSimilarity(s1, s2));
char s3[] = "ab";
char s4[] = "ba";
printf("%d\n", kSimilarity(s3, s4));
return 0;
}
c++完整代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <unordered_set>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int cost; // 代价,已经换了几回了!
int guess;// 猜测还要换几回,能变对!
int where;// 有必须去比对的下标,左边不再换了!
string str; // 当前的字符
Node(int r, int g, int i, string s) : cost(r), guess(g), where(i), str(s) {}
};
struct CompareNode {
bool operator()(const Node& a, const Node& b) {
return (a.cost + a.guess) > (b.cost + b.guess); // 小根堆
}
};
void swap(char& a, char& b) {
char tmp = a;
a = b;
b = tmp;
}
int evaluate(string s1, string s2, int index) {
int diff = 0;
for (int i = index; i < s1.size(); i++) {
if (s1[i] != s2[i]) {
diff++;
}
}
return (diff + 1) / 2;
}
void add(string add, string s2, int cost, int index, priority_queue<Node, vector<Node>, CompareNode>& heap,
unordered_set<string>& visited) {
if (!visited.count(add)) {
heap.push(Node(cost, evaluate(add, s2, index), index, add));
}
}
int kSimilarity(string s1, string s2) {
int len = s1.size();
priority_queue<Node, vector<Node>, CompareNode> heap;
unordered_set<string> visited;
heap.push(Node(0, 0, 0, s1));
while (!heap.empty()) {
Node cur = heap.top();
heap.pop();
if (visited.count(cur.str)) {
continue;
}
if (cur.str == s2) {
return cur.cost;
}
visited.insert(cur.str);
int firstDiff = cur.where;
while (cur.str[firstDiff] == s2[firstDiff]) {
firstDiff++;
}
string curStr = cur.str;
for (int i = firstDiff + 1; i < len; i++) {
if (curStr[i] == s2[firstDiff] && curStr[i] != s2[i]) {
swap(curStr[firstDiff], curStr[i]);
add(curStr, s2, cur.cost + 1, firstDiff + 1, heap, visited);
swap(curStr[firstDiff], curStr[i]);
}
}
}
return -1;
}
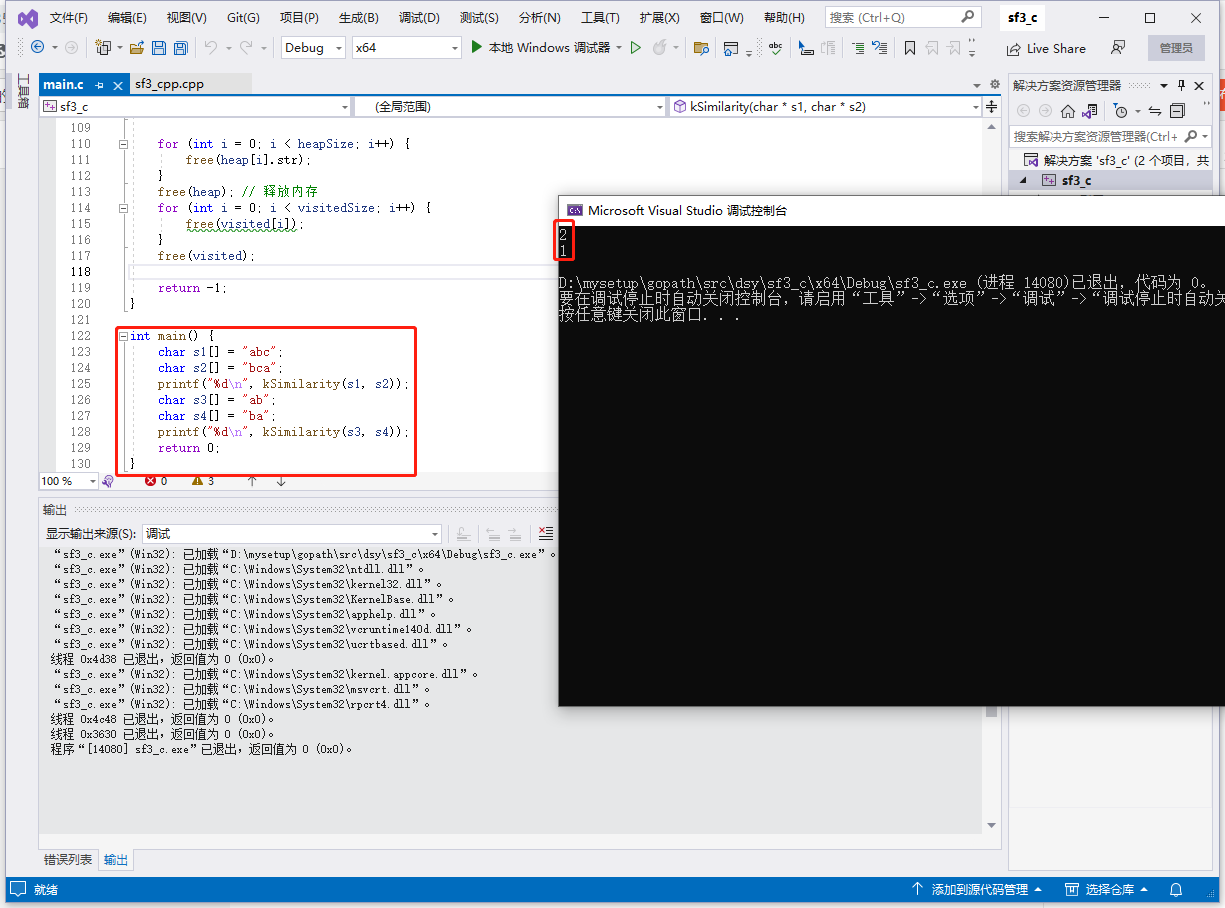
int main() {
string s1 = "abc";
string s2 = "bca";
cout << kSimilarity(s1, s2) << endl;
s1 = "ab";
s2 = "ba";
cout << kSimilarity(s1, s2) << endl;
}